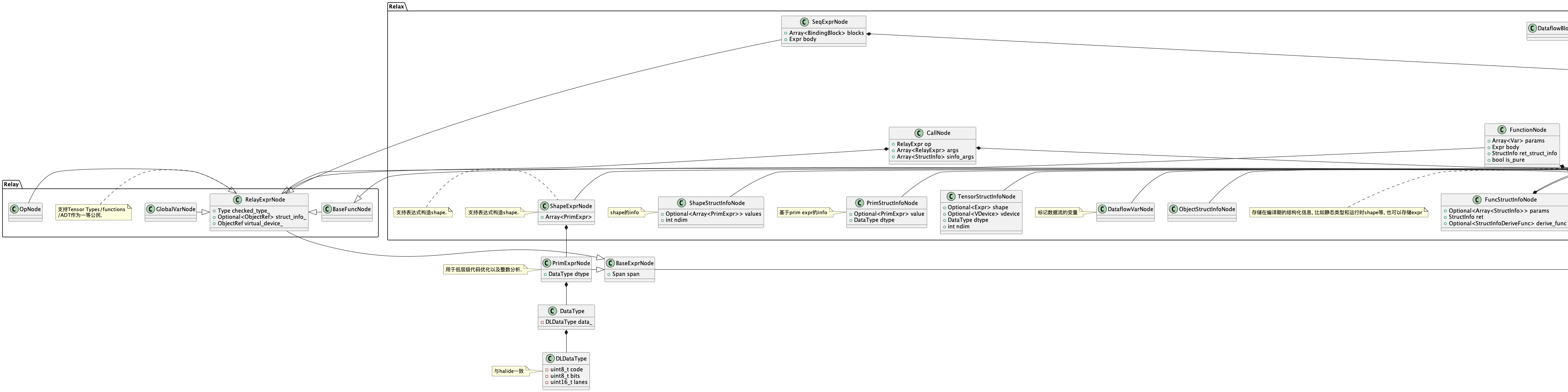
Function(
params=[
Var(
name_hint="a",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
),
Var(
name_hint="b",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=1,
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)]
)
)
)
)
],
body=SeqExpr(
blocks=[
BindingBlock(
bindings=[
VarBinding(
var=Var(
name_hint="c",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
),
value=Call(
op=Op(name="relax.add"),
args=[
Var(
name_hint="a",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
),
Var(
name_hint="b",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=1,
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)]
)
)
)
)
],
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
)
)
]
)
],
body=Var(
name_hint="c",
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
),
struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
)
),
ret_struct_info=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
),
is_pure=1,
attrs={"global_symbol": "fn1"},
struct_info=FuncStructInfo(
params=[
TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
),
TensorStructInfo(
dtype=float32,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=1,
values=[PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(1)`)]
)
)
)
],
ret=TensorStructInfo(
dtype=,
shape=ShapeExpr(
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
],
struct_info=ShapeStructInfo(
ndim=2,
values=[
PrimExpr(value=`n`),
PrimExpr(value=`T.int64(10)`)
]
)
)
),
purity=True
)
)
|